Energy Insider: China Approves 11 Nuclear Power Reactors, Curbs Coal Power Expansion
Listen to the full version

In this week’s Caixin energy wrap, we analyze China’s biggest climate and energy news on policy, industry, projects and more:
●China continues strong push for nuclear power
●Coal power plant approvals see sharp drop
●Beijing vows to defend EV-makers
●Mixed performance for “new three” exports
●State planner orders energy equipment upgrades
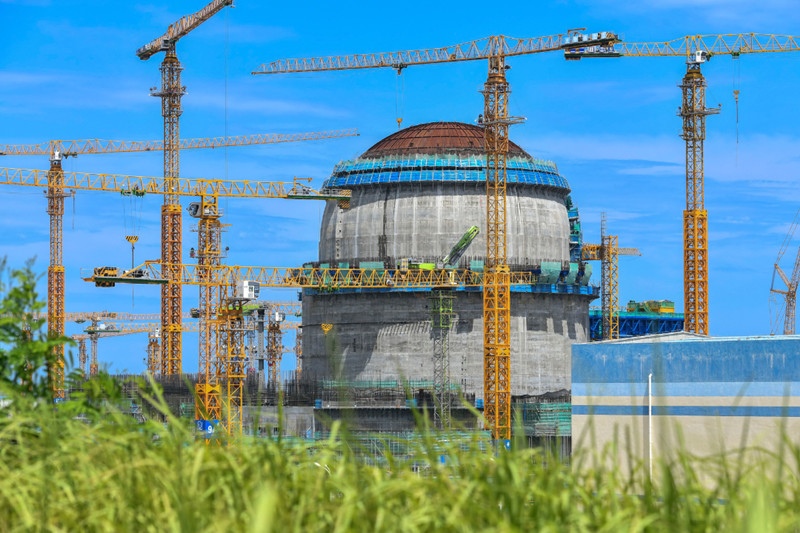
In focus: China approves 11 nuclear power reactors
What’s new: China has greenlighted the construction of 11 new nuclear power reactors in one go, as the central government continues its expansion of the energy source.
Download our app to receive breaking news alerts and read the news on the go.
Get our weekly free Must-Read newsletter.
- DIGEST HUB
- China approved the construction of 11 new nuclear reactors, estimated to cost over ¥200 billion ($28 billion), continuing its rapid nuclear expansion.
- Coal power plant approvals dropped significantly, down 79.5% year-on-year, indicating a potential shift in China's energy transition.
- Beijing vowed to defend Chinese EV makers against EU tariff hikes, while data showed mixed export performance for EVs, lithium-ion batteries, and solar cells.
China has set significant strides in its energy and climate policies this week, demonstrating contrasting dynamics within its energy sector. [para. 1]
**Nuclear Power Push:**
China has approved the construction of 11 new nuclear reactors, emphasizing its commitment to expanding nuclear energy capacity. Approved in a high-level meeting led by Premier Li Qiang, these reactors will be distributed across five coastal provinces: Jiangsu, Shandong, Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Guangxi. The total cost is projected to surpass 200 billion yuan ($28 billion). This move is part of China's accelerated expansion in nuclear power, a sector where it leads globally in growth rate. By 2030, China is expected to surpass the U.S. and France in the number of operational nuclear reactors. The latest approvals make 2024 the second-highest year for new reactor approvals, second only to 2008 when 14 reactors were greenlit. [para. 2][para. 3][para. 4]
**Coal Power Slowdown:**
Conversely, China’s coal power expansion has significantly decelerated. Only 10.34 gigawatts (GW) of new coal power capacity were approved between January and June, marking a 79.5% year-on-year decrease, as reported by Greenpeace East Asia. Similarly, the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air reported an 83% drop in coal power permits from the previous year, with only 9 GW approved in the first half of this year. This halt highlights a possible pivot in China’s energy strategy, focusing more on renewables and less on coal, a critical period in its energy transition. Whether the slowdown is due to an excess of already approved coal projects or a sign of a declining reliance on coal remains uncertain. [para. 5][para. 6]
**EV Sector and Trade Tensions:**
China reacted strongly against the European Commission's plan to impose elevated tariffs on Chinese-made electric vehicles (EVs), labeling the move as “unreasonable.” The revised tariff hikes target multiple Chinese automakers, with companies like SAIC Motor Corp. Ltd., Geely Automobile Holdings Ltd., and BYD Co. Ltd. facing additional duties ranging from 17% to 36.3%. In contrast, Tesla Inc. will incur a 9% tariff, lower than its competitors due to fewer subsidies from the Chinese government. These developments come amid ongoing investigations into state subsidies that allegedly allow Chinese manufacturers to undercut European competitors. [para. 7][para. 8][para. 9][para. 10]
**Mixed Export Performance:**
China’s “new three” green transition products exhibited mixed export performances in July. While exported EVs saw a 38.7% increase in volume and 19.8% growth in value, the export values of lithium-ion batteries and solar cells diverged. Lithium-ion battery exports remained nearly flat in volume but increased 7% in value to $5.4 billion. Solar cell units surged by 28.5% in exports, but their value dropped by 18.3% to $2.6 billion. The divergence in performance reflects the complexity as Chinese manufacturers navigate external trade pressures and domestic market dynamics marked by overcapacity and slowing demand. [para. 11][para. 12]
**Energy Equipment Upgrades:**
The central government has called for substantial investments to upgrade energy sector equipment, including coal power units and wind turbines. By 2027, investment volumes are expected to increase by one-quarter from 2023 levels, as outlined by the National Development and Reform Commission and the National Energy Administration. This initiative aims to bolster consumption and accelerate the energy transition, aligned with directives from a July State Council meeting focused on unleashing domestic demand potential. A trade-in program for new-energy vehicles, initiated in April, has already led to a surpassing of fossil fuel car sales as of July. [para. 13][para. 14]
In summary, China is making significant advancements in diversifying its energy portfolio, balancing nuclear expansion with a coal power slowdown, while addressing external trade challenges and pushing for technological upgrades in its energy infrastructure. [para. 1][para. 3][para. 4][para. 5][para. 6][para. 7][para. 8][para. 9][para. 10][para. 11][para. 12][para. 13][para. 14]
- SAIC Motor Corp. Ltd.
- SAIC Motor Corp. Ltd., the owner of MG, is facing an additional 36.3% duty on electric vehicles (EVs) exported to the European Union. This adjusted tariff forms part of an EU investigation that found Chinese state subsidies enable local EV-makers to undercut European competitors.
- Geely Automobile Holdings Ltd.
- Geely Automobile Holdings Ltd., parent company of Volvo Car AB, faces a proposed EU tariff hike of 19.3% on electric vehicle (EV) exports from China. This tariff is part of an ongoing European Commission investigation into Chinese state subsidies for EV makers. The new duties are slightly revised from provisional levels and come amid broader trade tensions.
- BYD Co. Ltd.
- BYD Co. Ltd. is a Chinese electric vehicle (EV) maker facing a 17% additional duty on EVs shipped to the EU, following the European Commission’s investigation into state subsidies. This tariff hike is part of the EU's adjusted plan to impose higher duties on China-made EVs, with overall tariffs intended to address undercutting of European rivals enabled by Chinese state subsidies.
- Tesla Inc.
- Tesla Inc. will face a relatively lower 9% tariff on its electric vehicles exported to Europe, compared to higher tariffs imposed on Chinese competitors. This lower tariff is partly due to Beijing providing fewer subsidies to foreign-owned companies like Tesla, according to the European Commission's investigation findings.
- April 2024:
- China introduces a trade-in program for EVs.
- July 2024:
- Trade-in program helps new-energy vehicles eclipse fossil fuel cars in monthly sales for the first time.
- Aug. 18, 2024:
- General Administration of Customs releases data showing July 2024 export performance for EVs, lithium-ion batteries, and solar cells.
- Aug. 19, 2024:
- High-level meeting presided by Premier Li Qiang approves the construction of 11 new nuclear power reactors.
- Aug. 19, 2024:
- Global Energy Monitor releases a report highlighting China's rapid nuclear power capacity expansion.
- Aug. 20, 2024:
- Greenpeace East Asia releases a report detailing a 79.5% decrease in new coal power capacity approvals between January and June 2024.
- Aug. 21, 2024:
- National Development and Reform Commission and the National Energy Administration release a notice calling for increased investments in energy equipment upgrades by a quarter from 2023 levels by 2027.
- Aug. 22, 2024:
- Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air releases a report showing an 83% year-on-year drop in coal power permits in the first half of 2024.
- Date not specified, Tuesday:
- European Commission announces an adjusted set of proposed tariff hikes on China-made EVs.
- PODCAST
- MOST POPULAR







 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google
 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with 财新
Sign in with 财新