Latest Cover Story | Where is the Cure for Obesity? (AI Translation)
Listen to the full version

文|财新周刊 崔笑天 蒋模婷
By Caixin Weekly‘s Cui Xiaotian and Jiang Moting
文|财新周刊 崔笑天 蒋模婷
By Caixin Weekly's Cui Xiaotian and Jiang Moting
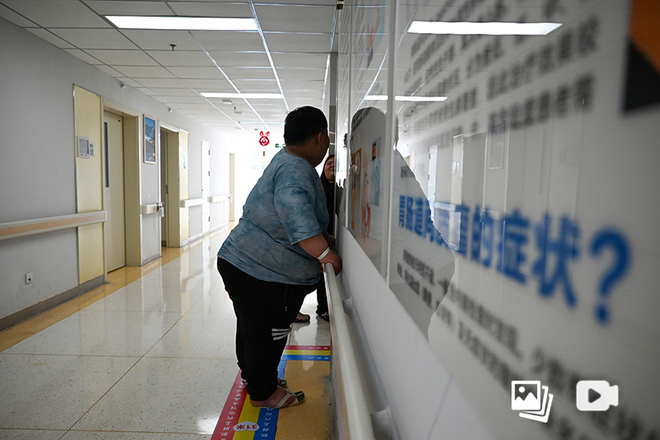
今年8月17日,名为“中国肥胖大会”的学术活动,已经是第三次启幕。减重与代谢外科、内分泌代谢科、临床营养科、心血管内科、代谢生物学、公共卫生等跨多个学科和领域的医者、学者齐聚北京市建筑规模庞大的国家会议中心,分享新研究、新方法、新发现,共同探讨肥胖防治的有效对策。
On August 17th this year, the academic event named the "China Obesity Congress" commenced for the third time. Physicians and scholars specializing in bariatric and metabolic surgery, endocrinology and metabolism, clinical nutrition, cardiology, metabolic biology, public health, and other disciplines gathered at the substantial National Convention Center in Beijing. They shared new research, methods, and discoveries, collectively discussing effective strategies for the prevention and treatment of obesity.
大会首次召开是在2021年7月,当时由国家消化系统疾病临床医学研究中心(北京)、北京医师协会减重与代谢专科医师分会联合主办。当年6月,美国批准了由丹麦制药商诺和诺德推出的GLP-1(胰升糖素样肽-1)受体激动剂司美格鲁肽作为减肥药上市。大会希望推动肥胖症的科研与临床探索,解决肥胖问题;历年各有侧重,从最初的希望让更多人认识到肥胖是一种疾病,到倡导科学应对肥胖,再到如今的肥胖治疗多学科协作与体重管理中心的建设,愈发“接地气”。
The inaugural conference was held in July 2021, co-hosted by the National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases (Beijing) and the Beijing Medical Association's Weight and Metabolic Specialist Physicians Branch. In June of that year, the U.S. approved the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonist semaglutide, produced by Danish pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk, for the market as a weight-loss drug. The conference aimed to advance research and clinical exploration of obesity to address the issue. Each year, the conference has had different focal points, from initially raising awareness that obesity is a disease, to advocating scientific approaches to address obesity, and now focusing on multidisciplinary collaboration in obesity treatment and the establishment of weight management centers, reflecting an increasingly grounded approach.
- DIGEST HUB
- The "China Obesity Congress" highlighted multidisciplinary collaboration and new weight-loss drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide.
- GLP-1 drugs have surpassed previous weight-loss medications, showing significant efficacy in clinical trials.
- Obesity treatment in China is evolving, with updated guidelines advocating for early and long-term management, yet challenges remain in public acceptance and healthcare integration.
The academic event "China Obesity Congress," held on August 17 this year, marked its third occurrence, gathering experts from various fields to discuss obesity prevention and treatment strategies [para. 1]. The inaugural conference, held in July 2021, was initiated to advance obesity research, particularly with the approval of the weight-loss drug semaglutide in the U.S. Different aspects of obesity were highlighted each year, from raising awareness to focusing on scientific and multidisciplinary approaches [para. 2].
As of May 2023, significant advancements in drugs targeting GLP-1 for obesity treatment were evident, with Eli Lilly's Tirzepatide entering the Chinese market for diabetes treatment and attracting over 1,200 participants to this year's congress [para. 3]. Historically, obesity booths were dominated by medical device companies, but now pharmaceutical firms lead [para. 5]. GLP-1 medications emerged as superior in safety and efficacy compared to previous weight-loss drugs like fenfluramine and sibutramine [para. 6]. Before the advent of GLP-1 medications, orlistat was the sole clinically available weight-loss drug; however, GLP-1 drugs prove more effective by acting as natural appetite suppressants [para. 7].
Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, notable GLP-1 drugs, were approved for weight loss in China in 2024, with clinical data showing significant weight loss and additional health benefits [para. 10]. Global obesity rates present a growing public health problem, with over two billion adults classified as overweight or obese [para. 13]. In China, obesity is particularly severe, with half the population overweight or obese by 2018, and projections indicating 70% of the population will be overweight by 2030 [para. 15]. BMI is a key metric for assessing obesity [para. 16]. The health impact of obesity includes risks of diabetes, hypertension, and reduced life expectancy [para. 19].
Stigma surrounding obesity remains a major issue, often linking obesity with personal failings rather than recognizing it as a disease [para. 22]. New medications like semaglutide have shown promising results in weight loss, leading to significant health and emotional benefits [para. 23]. Updated guidelines from the Chinese Society of Endocrinology in July 2024 emphasize early and long-term weight management [para. 25]. Obesity management involves complex, chronic conditions requiring continuous medical intervention [para. 26]. The World Health Organization aims to release new guidelines integrating drug therapies with lifestyle and nutritional interventions [para. 28].
The establishment of specialized weight management centers and interdisciplinary collaboration is vital for effective obesity treatment [para. 29]. The "Weight Management Year" plan introduced nationally in June 2024 aims to mobilize societal efforts for comprehensive weight management [para. 31]. Effective obesity guidelines need to address long-term management and involve multidisciplinary cooperation to prevent weight rebound [para. 44].
Treating obesity also involves addressing the "weight set point" phenomenon, where the body naturally resists weight loss, leading to rebounds [para. 49]. Continuous medication usage is crucial for maintaining weight loss, with lifestyle interventions and exercise playing supportive roles [para. 55]. Side effects and long-term reliance on drugs remain a concern, highlighting the need for balanced treatment approaches [para. 64].
The integration of lifestyle changes and medication, alongside proper clinical guidelines, underscores the importance of comprehensive and continued weight management for effective health outcomes [para. 73]. The ongoing challenges include ensuring effective cooperation among various medical disciplines and adapting to new treatment methodologies to provide holistic care for obesity patients [para. 84].
- Novo Nordisk
- Novo Nordisk is a Danish pharmaceutical company that introduced the GLP-1 receptor agonist Semaglutide as a weight loss drug, approved in the U.S. in June 2021. It has since gained significant prominence, with global sales approaching those of leading anti-tumor drugs. Semaglutide was approved for weight loss in China in June 2024. This drug marked a significant advancement in obesity treatment, providing both safety and efficacy.
- Eli Lilly
- Eli Lilly, a multinational pharmaceutical company, introduced the GLP-1/GIP dual-target drug tirzepatide, approved for weight loss in China in July 2024. This drug targets GLP-1 and GIP, theoretically offering superior effects in regulating energy metabolism.
- East China Pharmaceutical
- East China Pharmaceutical's bioequivalent drug Liraglutide was approved in July 2023 as one of the four GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) medications for weight loss in China.
- Renhe Biotechnology
- Renhe Biotechnology developed a domestically produced GLP-1 weight loss drug called Benaluraglutide, which was approved in July 2023. This adds to the available GLP-1 medications for weight loss in China, joining other drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide.
- Shanghai Yaoying Medical
- Shanghai Yaoying Medical's Endocrinology, Metabolism, and Thyroid Center is led by Director Xu Shen and is involved in the development of clinical guidelines for obesity. The center aims for early treatment and personalized management of obesity, aligning with European expert consensus on effective reforms in weight management and chronic endocrinological metabolic diseases.
- June 2021:
- The U.S. approved semaglutide for the market as a weight-loss drug.
- July 2021:
- The inaugural 'China Obesity Congress' was held.
- By 2023:
- GLP-1 drugs largely displaced orlistat as the primary clinically available weight-loss medication.
- May 2024:
- Eli Lilly's GLP-1/GIP dual-target drug, Tirzepatide, entered China with approval for diabetes treatment.
- June 2024:
- Semaglutide was approved for weight loss in China.
- July 2024:
- Tirzepatide was approved for weight loss in China.
- July 2024:
- The Chinese Society of Endocrinology unveiled updated guidelines for weight management.
- August 17, 2024:
- The 'China Obesity Congress' commenced for the third time.
- August 26, 2024:
- WHO Chief Scientist Jeremy Farrar indicated that new WHO guidelines would be released soon.
- PODCAST
- MOST POPULAR





 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google
 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with 财新
Sign in with 财新