How to Address the Issue of Chinese People Becoming Increasingly Obese(AI Translation)
Listen to the full version

文|财新周刊 崔笑天 蒋模婷
By Caixin Weekly's Cui Xiaotian and Jiang Moting
今年8月17日,名为“中国肥胖大会”的学术活动,已经是第三次启幕。减重与代谢外科、内分泌代谢科、临床营养科、心血管内科、代谢生物学、公共卫生等跨多个学科和领域的医者、学者齐聚北京市建筑规模庞大的国家会议中心,分享新研究、新方法、新发现,共同探讨肥胖防治的有效对策。
On August 17 this year, the academic event named the "China Obesity Conference" commenced for the third time. Physicians and scholars from diverse disciplines and fields, including bariatric and metabolic surgery, endocrinology and metabolism, clinical nutrition, cardiovascular medicine, metabolic biology, and public health, gathered at the expansive China National Convention Center in Beijing. They shared new research, methods, and discoveries, and jointly discussed effective strategies for obesity prevention and treatment.
大会首次召开是在2021年7月,当时由国家消化系统疾病临床医学研究中心(北京)、北京医师协会减重与代谢专科医师分会联合主办。当年6月,美国批准了由丹麦制药商诺和诺德推出的GLP-1(胰升糖素样肽-1)受体激动剂司美格鲁肽作为减肥药上市。大会希望推动肥胖症的科研与临床探索,解决肥胖问题;历年各有侧重,从最初的希望让更多人认识到肥胖是一种疾病,到倡导科学应对肥胖,再到如今的肥胖治疗多学科协作与体重管理中心的建设,愈发“接地气”。
The conference was first convened in July 2021, jointly organized by the National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases (Beijing) and the Metabolic and Bariatric Doctor Division of the Beijing Medical Doctor Association. In June of the same year, the U.S. approved Danish pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk's GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonist, Semaglutide, for weight loss. The aim of the conference is to promote research and clinical exploration of obesity to address the condition. Each year, the focus has varied, from initially hoping to increase awareness that obesity is a disease, to advocating scientific approaches to obesity, and now emphasizing multidisciplinary collaboration in obesity treatment and the establishment of weight management centers, making the efforts increasingly grounded.
三年之中,以GLP-1为靶点的药物你追我赶。今年5月,跨国药企礼来的GLP-1/GIP(葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽)双靶点药物替尔泊肽凭借降糖适应证入华,又为火热的药物减肥赛道添了一把柴。中国肥胖大会主席、北京友谊医院副院长、国家消化系统疾病临床医学研究中心副主任张忠涛介绍,今年会议的注册人数已经超过1200人,而以往只有300—400人。
Within the past three years, medications targeting GLP-1 have been fiercely competitive. This May, multinational pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly introduced its dual GLP-1/GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) targeting drug, tirzepatide, to China for its glucose-lowering indication, adding fuel to the already intense race in the weight-loss drug sector. Zhang Zhongtao, chairman of the China Obesity Conference, deputy director of Beijing Friendship Hospital, and deputy director of the National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases, noted that this year's conference registration has exceeded 1,200 participants, compared to only 300-400 in previous years.
- DIGEST HUB
- The China Obesity Conference, held for the third time, focused on multidisciplinary collaboration in obesity treatment, attracting over 1,200 participants this year.
- GLP-1 drugs, such as Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, have revolutionized weight loss treatment, outperforming previous weight loss medications in safety and efficacy.
- The event emphasized that obesity is a complex chronic disease requiring systematic, multidisciplinary management and proposed centralized weight management centers in hospitals.
The article details the third annual "China Obesity Conference," held on August 17 at the China National Convention Center in Beijing, where a variety of professionals from different medical fields gathered to share and discuss new research and strategies for obesity prevention and treatment. The event, organized initially in July 2021 by Beijing’s National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases and the Metabolic and Bariatric Doctor Division of the Beijing Medical Doctor Association, aims to propel obesity research and encourage a multidisciplinary approach [para. 1][para. 3].
Since its inception, the conference has rapidly grown, with registrations expanding from 300-400 in early years to over 1,200 in 2023. Notably, GLP-1 receptor agonists have emerged as prominent in obesity treatment. Eli Lilly's dual GLP-1/GIP targeting drug, tirzepatide, introduced in China for glucose-lowering, has intensified the competition in this sector. Also significant are exhibitor changes at the conference, with pharmaceutical companies now predominating and showcasing the latest weight-loss drugs and surgical devices [para. 1][para. 3][para. 4].
Over the past decade, GLP-1 drugs have become highly favored due to their effectiveness and safety profile compared to previous weight-loss drugs like fenfluramine and sibutramine. Originally aimed at lowering blood sugar, four GLP-1 medications are currently available in China, with semaglutide and tirzepatide being notable examples. Clinical studies show these drugs can achieve up to 22.5% in weight reduction over one and a half years. They’re praised not only for promoting significant weight loss but also for improving cardiovascular health, kidney function, and conditions like sleep apnea [para. 4][para. 6][para. 7][para. 8].
Worldwide, over two billion adults are overweight or obese. In China, obesity rates have significantly increased; half the population was overweight or obese by 2018, a threefold increase from 2004. The trend, especially among the young, is alarming. The BMI thresholds for overweight and obesity in China are lower than international standards, reflecting the higher risk Asians face for complications at lower levels of obesity [para. 8][para. 10][para. 11].
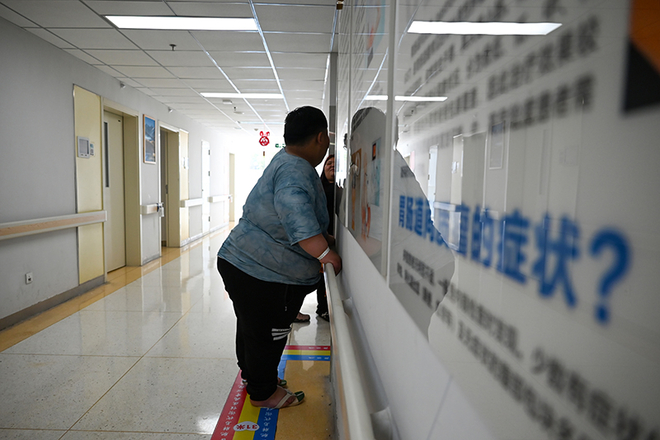
Despite its prevalence, recognizing obesity as a disease remains a challenge. Beyond physical health risks like diabetes and heart disease, obesity carries a social stigma. Emotional and psychological impacts are widespread, with many obese individuals experiencing bullying, exclusion, and deep psychological distress. Effective treatment now includes not just lifestyle changes, but also new medications and supportive social environments [para. 12][para. 13][para. 14][para. 15][para. 16].
Updated clinical guidelines now advocate for earlier intervention with medications and stress long-term weight management. The "Guidelines for Long-term Weight Management and Clinical Application of Drugs in Obese Patients" released in July 2024 emphasize combining lifestyle interventions with medication from the outset. This approach aligns with international expert consensus and seeks to mitigate the cyclical struggle of weight loss and regain that many patients face [para. 16][para. 17][para. 18].
Significant advancements in obesity treatment necessitate a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach involving endocrinology, bariatric surgery, nutrition, and psychology. Hospitals are encouraged to create centralized weight management centers to provide holistic and sustained care. The National Health Commission’s "Weight Management Year" Activity Implementation Plan, issued in June 2024 with support from multiple governmental ministries, underscores the importance of raising public awareness and promoting effective weight management across all life stages [para. 19][para. 21][para. 22].
The systemic and ingrained nature of obesity demands coordinated efforts across societal and governmental frameworks. Moving forward, the integration of multidisciplinary treatments, combined with new pharmaceutical developments, offers hope for effective and sustained obesity management, transforming public health outcomes on a broad scale [para. 22][para. 24][para. 25][para. 26].
- Novo Nordisk
诺和诺德 - Novo Nordisk, a Danish pharmaceutical company, introduced the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide for weight loss, approved in the U.S. in June 2021. The drug, mimicking natural GLP-1, effectively suppresses appetite and prolongs fullness. It has gained widespread use for obesity treatment, even outperforming former weight-loss drugs. Semaglutide is expected to be approved for weight loss in China by June 2024.
- Eli Lilly
礼来 - Eli Lilly is a multinational pharmaceutical company mentioned in the article for its GLP-1/GIP dual-target drug Tirzepatide, which entered the Chinese market in May under a diabetes indication. This drug, seen as a "challenger," also targets both GLP-1 and GIP, potentially offering superior efficacy in managing weight. Tirzepatide was approved for weight loss in China in July 2024.
- East China Pharmaceutical
华东医药 - East China Pharmaceutical has developed a GLP-1 drug called liraglutide, a biosimilar for weight loss, which was approved in July 2023. This drug is part of the newer generation of weight management medications targeting obesity and diabetes, showing promising results in clinical treatments.
- Revenio Biosciences
仁会生物 - The article content does not mention Revenio Biosciences. It focuses on the third "China Obesity Conference" and discussions on obesity treatments, including new pharmaceuticals like GLP-1 receptor agonists, and multi-disciplinary approaches to obesity management in China.
- June 2021:
- The U.S. approved Danish pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk's GLP-1 receptor agonist, Semaglutide, for weight loss.
- July 2021:
- The first China Obesity Conference was convened.
- By 2023:
- The only clinically available weight loss drug was the fat absorption inhibitor orlistat.
- July 2023:
- Hua Dong Medicine's biosimilar liraglutide and Genor Biopharma's newly developed domestic drug benaglutide were approved.
- June 2024:
- The National Health Commission, along with 16 other ministries, jointly issued the 'Weight Management Year' Activity Implementation Plan.
- June 2024:
- Semaglutide was approved for weight loss in China.
- July 2024:
- Eli Lilly's tirzepatide was approved for weight loss in China.
- July 2024:
- The Chinese Society of Endocrinology released new guidelines for drug treatment in obesity management.
- August 17, 2024:
- The third China Obesity Conference commenced.
- August 26, 2024:
- WHO Chief Scientist Jeremy Farrar announced that the WHO will soon release new guidelines integrating new-generation weight-loss medications, lifestyle interventions, and nutritional adjustments.
- PODCAST
- MOST POPULAR





 Sign in with Google
Sign in with Google
 Sign in with Facebook
Sign in with Facebook
 Sign in with 财新
Sign in with 财新